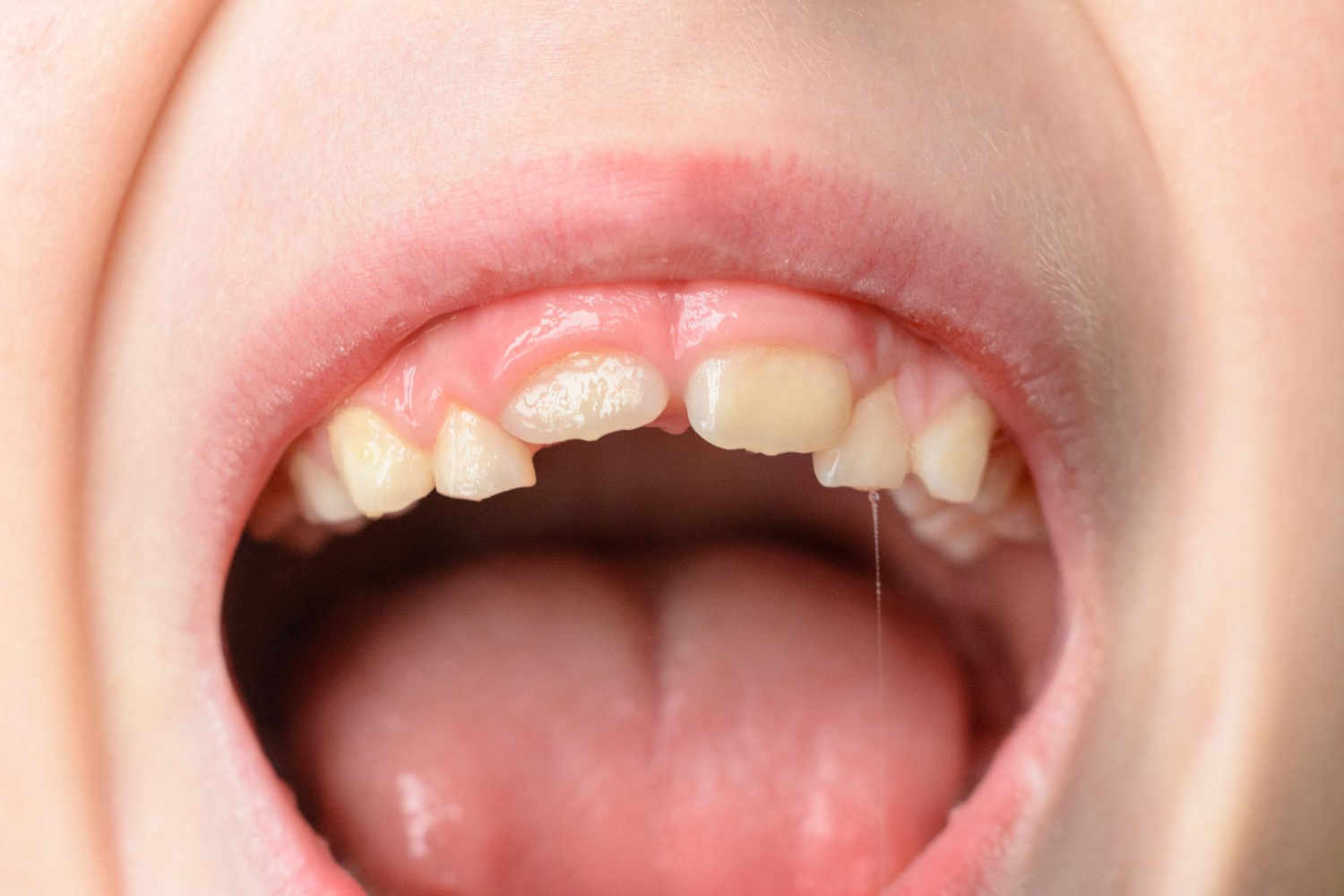
Swollen Gums: Symptoms, Causes, Treatments & Preventions
Swollen gums refer to the condition where the gums around the teeth become inflamed and swollen. It can affect people of all ages and can arise due to multiple causes. Swollen gums can range in severity from mild to severe, affecting one or more areas of the mouth. In some cases, swollen gums may accompany other symptoms such as redness, tenderness, and bleeding.
It’s essential to address swollen gums as soon as possible, as they can be a sign of underlying oral health issues that need to be addressed. If left untreated, swollen gums can lead to more severe problems such as tooth loss, gum disease, and even systemic health issues. But don’t worry; with proper oral hygiene and treatment, it’s possible to manage and prevent swollen gums. In this article, we’ll discuss the various causes of swollen gums, the signs to look out for, and the steps you can take to keep your mouth healthy and comfortable.
Causes of swollen gums
There are several possible causes of swollen gums. Some of the most common causes include:
Gingivitis: This is a common form of gum disease caused by poor oral hygiene. When you don’t clean your teeth regularly, a sticky film of bacteria called plaque can build up on your teeth. This plaque can irritate your gums, causing them to become inflamed and swollen. Your gums may be red, swollen, and tender if you have gingivitis, and you may notice bleeding when you brush your teeth.
Pregnancy: Hormonal changes during pregnancy can cause your gums to become more sensitive and prone to inflammation. This is called pregnancy gingivitis. See a dentist or medical professional if you are pregnant and have swollen gums.
Infection: Bacterial infections, such as a dental abscess, can cause your gums to become swollen and painful. A dental abscess is a pocket of pus that forms in the mouth when bacteria infect an area around the tooth. If you have a dental abscess, you may notice swelling in your gums, a bad taste in your mouth, and pain when you eat or drink. A dental abscess is a serious problem that needs to be treated as early as possible.
Malnutrition: Lack of essential nutrients in your diet can cause your gums to become swollen and prone to infection. Nutrients such as vitamin C and calcium are important for healthy gums. If you are not getting enough of these nutrients in your diet, your gums may become swollen and prone to infection. It’s essential to eat a well-balanced diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, and other sources of nutrients to keep your gums healthy.
Risk factors for swollen gums
Gingivitis is a common condition that can affect anyone. The following factors can increase your risk of gingivitis:
- Poor oral hygiene habits
- Tobacco use, whether smoking or chewing
- Older age
- Dry mouth
- Poor nutrition, including a lack of vitamin C
- Missing dental restorations or crooked teeth that are difficult to clean
- Immune-suppressing conditions, such as leukemia, HIV/AIDS, or cancer treatment
- Certain medications, such as phenytoin used to treat epileptic seizures, and some calcium channel blockers used to treat angina, high blood pressure, and other conditions.
- Hormonal changes, such as those associated with pregnancy, the menstrual cycle, or the use of birth control pills
Symptoms
The most common symptoms of swollen gums include:
Redness: Swollen gums may appear red or pinkish.
Swelling: The gums may be swollen and puffy, particularly around the teeth.
Tenderness: The gums may be tender to the touch or painful when you eat or drink.
Bleeding: The gums may bleed when you brush your teeth or floss.
Bad breath: Swollen gums can sometimes cause bad breath or a bad taste in the mouth.
Loose teeth: In severe cases of gum disease, the gums may recede, and the teeth may become loose.
If you have any of these symptoms, you must see a dentist or medical professional for an evaluation.
Diagnosis of swollen gums
If you have swollen gums, your dentist or medical professional will thoroughly examine the cause of your symptoms. This may include:
Dental history: Your dentist will ask about your dental history, including any previous dental work, medications you are taking, and any medical conditions you have.
Physical examination: Your dentist will examine your mouth, including your teeth, gums, and tongue. They will look for signs of swelling, redness, tenderness, and bleeding.
Dental x-rays: Your dentist may take x-rays of your teeth to look for signs of infection or other underlying issues.
Gum pocket measurements: Your dentist may measure the depth of the pockets between your gums and teeth to assess the severity of your gum disease.
Blood tests: In some cases, your dentist may recommend blood tests to check for medical conditions or infections that could be causing your swollen gums.
Based on the results of these tests, your dentist can diagnose the cause of your swollen gums and recommend a treatment plan.
Treatment of swollen gums
If you have swollen gums, your dentist or medical professional will develop a treatment plan to help alleviate your symptoms and improve the health of your gums. Here are some common treatment options:
Dental cleaning: This is a common treatment for gum disease, a common cause of swollen gums. During a dental cleaning, your dentist will use special tools to remove plaque and tartar (a hardened form of plaque) from your teeth and gums. This can help reduce inflammation and swelling in the gums.
Dental restoration: If you have damaged teeth or fillings, your dentist may recommend repairing or replacing them. This can help prevent further irritation of the gums and improve the overall health of your mouth.
Ongoing care: Your dentist may recommend regular teeth cleanings and check-ups to help prevent gum disease and maintain healthy gums. They may also recommend using an antimicrobial mouthwash or special toothpaste to help kill bacteria and reduce inflammation in the gums.
In addition to medical treatment, there are several things you can do at home to help improve the health of your gums.
Home remedies for swollen gums
To help relieve your swollen gums, try one of the following home remedies:
Saltwater
A saltwater rinse can reduce inflammation and promote the healing of the gums.
- Mix 1 teaspoon of salt and 8 ounces of lukewarm warm water.
- For 30 seconds, rinse your mouth with this saltwater solution.
- Do not swallow it; instead, spit it out.
- Repeat 2–3 times per day until the swelling subsides.
Cold compresses
Reduced blood flow can help reduce inflammation and swelling that causes pain. This can be achieved by cold compressing the affected area. To use a cold compress, follow these steps:
- Wrap a clean washcloth or towel around a bag of crushed ice and place it against your face for about 5 minutes.
- Repeat the warm/cold cycle 2–3 times more.
- Do this 2–3 times per day for the first two days after getting swollen gums.
It’s important to use a washcloth that is not too cold, as excessive cold can cause further irritation to the gums.
Warm compresses
The heat from a warm compress can help increase blood flow to the affected area thus improving the healing process. To use a warm compress, follow these steps:
- Soak a clean washcloth or towel in warm water and squeeze out the excess water.
- Hold the warm cloth against your face for about 5 minutes — outside the mouth, not directly on the gums.
This method is usually done when the pain is more bearable after the cold compress.
Turmeric gel
Curcumin, found in turmeric, has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. A study found that turmeric gel could help prevent plaque and gingivitis. Gingivitis is the most frequent cause of swollen gums.
- Rinse your mouth with clean water after brushing your teeth.
- Massage turmeric gel into your gums.
- Leave on your gums for 10 minutes.
- Swish some fresh water around your mouth to remove the gel.
- Do not swallow it; instead, spit it out.
- Do this twice a day until the swelling goes away.
Essential oils
Peppermint, tea tree, and thyme oil, according to a 2013 study, are effective in preventing the growth of disease-causing microorganisms in the mouth.
- Mix three drops of essential oil from peppermint, thyme, or tea tree with eight ounces of warm water.
- Swish the mixture around in your mouth for about 30 seconds to rinse.
- Do not swallow it; instead, spit it out.
- Do this twice a day until the swelling subsides.
Mouthwash containing chlorhexidine
Mouthwash is as effective in curing and preventing gingivitis. It contains chlorhexidine, a prescription treatment for gingivitis.
- Swish 2 teaspoons of mouthwash
- Do not swallow it; instead, spit it out.
- Do this twice a day for fourteen days.
It’s important to follow your medical professional’s recommendations for treatment and care to help alleviate your swollen gums and prevent further issues.
When to see a doctor?
See a dentist or medical professional if you have swollen gums, as it could be a sign of an underlying issue that needs to be addressed. Here are some specific situations in which you should seek medical attention for swollen gums:
You have symptoms of gum disease: If you have swollen gums that are red, tender, or bleed easily, it could be a sign of gum disease. Gum disease is a serious condition that can lead to tooth loss if left untreated.
You have other symptoms: If you have swollen gums and other symptoms such as fever, pain when eating or drinking, or difficulty breathing, it could be a sign of a more severe condition.
You have a dental abscess: A dental abscess is a pocket of pus that forms in the mouth when bacteria infect an area around the tooth. A dental abscess can be serious if left untreated, so it’s essential to see a dentist as soon as possible.
Your gums don’t improve with home treatment: See a dentist if you have swollen gums and try home treatment, but your gums don’t improve. They can help determine the cause of your swollen gums and recommend treatment to help alleviate your symptoms.
What to expect during the appointment?
During your appointment for swollen gums, your dentist may ask you various questions to diagnose the cause of your symptoms. Here are some questions your dentist may ask:
- How long have you had swollen gums?
- Do you brush and floss your teeth regularly?
- Do your gums bleed when you brush your teeth?
- Have you noticed any changes in the color or appearance of your gums?
- Do you have other symptoms, such as pain when eating or drinking, difficulty breathing, or a bad taste in your mouth?
- Have you had any recent dental work, such as fillings or extractions?
- Do you have any medical conditions?
- Do you smoke or use tobacco products?
Your answers to these questions and the dentist’s examination will lead to the cause of your swollen gums. Once the dentist has confirmed the diagnosis, they devise a treatment plan. Stick to it, follow the dentist’s advice, and maintain good oral hygiene.
Final words
Swollen gums can be a sign that something isn’t quite right in your mouth. Several things can cause swollen gums, such as gum disease, certain medications, and hormone changes. To determine what’s causing your swollen gums, your dentist will ask questions about your dental history and examine your mouth. They may also take x-rays or do some blood tests. The treatment for swollen gums will depend on what’s causing the swelling. It may include dental cleaning, fixing damaged teeth or fillings, and ongoing care.
If you have swollen gums, it’s essential to seek treatment from a dental professional. At Stellar Dental, our experienced team is dedicated to providing high-quality care to help alleviate your symptoms and improve the health of your gums. We offer flexible scheduling and a welcoming environment to make your visit as comfortable as possible. Don’t wait any longer to get the treatment you need. Contact Stellar Dental today to schedule an appointment.